American sellers on Amazon are losing market share to international sellers and are now making up less than 50% of the sellers.
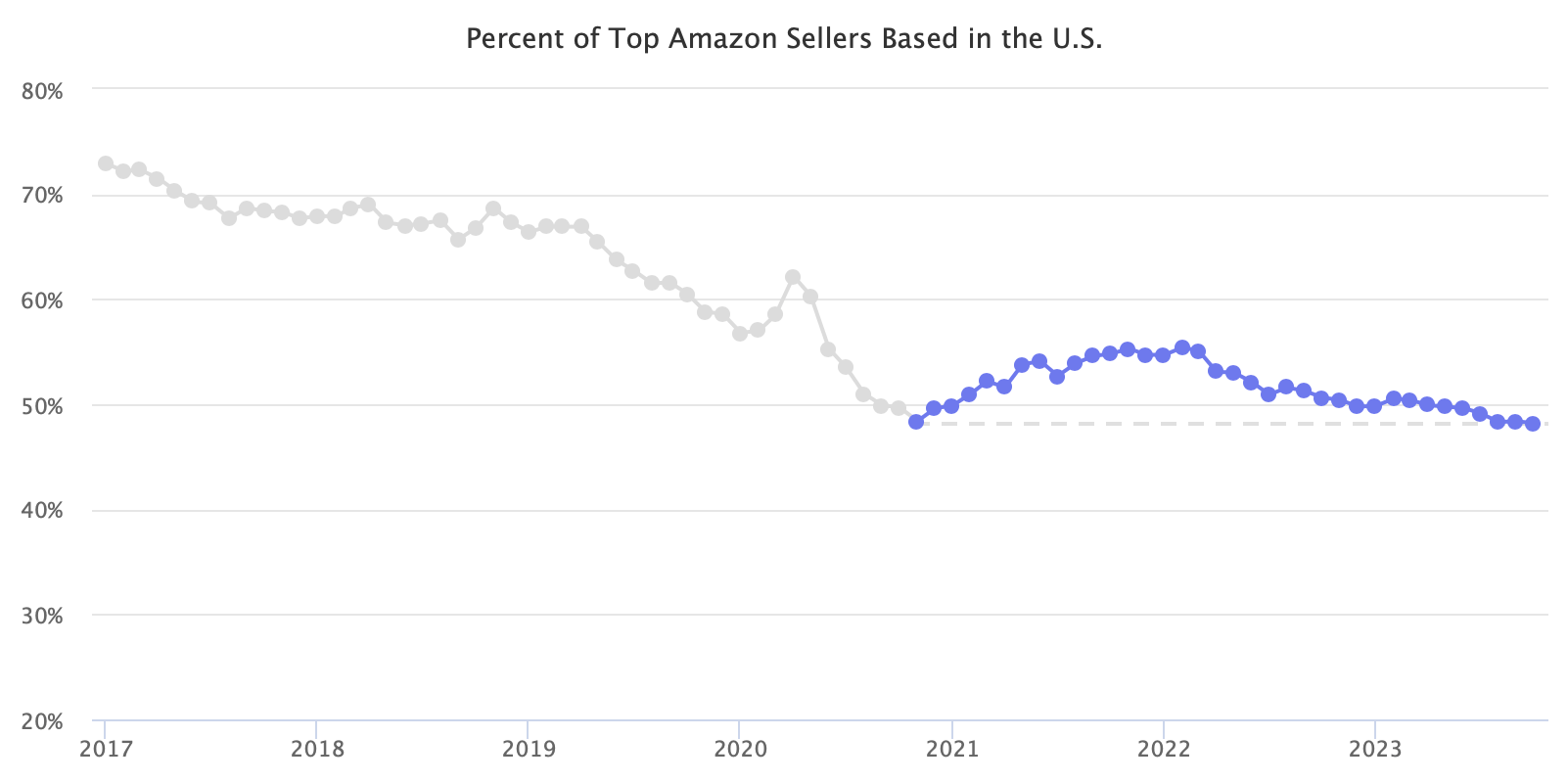
According to Marketplace Pulse research, 48% of the top third-party sellers on Amazon’s marketplace in the U.S. are American businesses. 48% is the lowest it has ever been. The recent high was 55% in March 2022, which it reached from the previous low in November 2020. The analysis was done on the top sellers because they represent a major share of the GMV and, as a group, are more informative than the total set of sellers.
Most sellers on the Amazon marketplace in the U.S. are domestic or Chinese businesses (other countries have a relatively small presence). Chinese sellers have been increasing their market share on Amazon for years. But in November 2020, likely caused by lockdowns, supply chain issues, seller suspensions, and Amazon FBA inventory limits, American sellers reversed the trend and started gaining market share.
However, the reversal stopped in March 2022 when it returned to the years-old trend. Chinese sellers have since regained lost market share and, in recent months, hit new highs. In turn, American sellers hit record lows.
Chinese sellers continue to do well on Amazon because virtually all use Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) to store and fulfill inventory, rendering their products Prime-eligible. The seller’s business address is thus only relevant as the location where the seller employs staff and pays most taxes. Consumers, by Amazon’s design, are oblivious to the whereabouts of sellers on Amazon.
While Amazon’s mass suspension of hundreds of top Chinese sellers in 2021 shocked the market, and new marketplaces like Shein and Temu appeared to offer a way out, Chinese sellers didn’t quit Amazon. The period from November 2020 to March 2022 was an anomaly. Amazon’s GMV is still the biggest, and thus, “Made in China, Sold on Amazon” is still the norm.

